
As large vision-language models (LVLMs) evolve rapidly, the demand for high-quality and diverse data to align these models becomes increasingly crucial. However, the creation of such data with human supervision proves costly and time-intensive. In this paper, we investigate the efficacy of AI feedback to scale supervision for aligning LVLMs. We introduce VLFeedback, the first large-scale vision-language feedback dataset, comprising over 82K multi-modal instructions and comprehensive rationales generated by off-the-shelf models without human annotations. To evaluate the effectiveness of AI feedback for vision-language alignment, we train Silkie, an LVLM fine-tuned via direct preference optimization on VLFeedback. Silkie showcases exceptional performance regarding helpfulness, visual faithfulness, and safety metrics. It outperforms its base model by 6.9% and 9.5% in perception and cognition tasks, reduces hallucination issues on MMHal-Bench, and exhibits enhanced resilience against red-teaming attacks. Furthermore, our analysis underscores the advantage of AI feedback, particularly in fostering preference diversity to deliver more comprehensive improvements.
 Multimodal Instructions and AI Preference Data
Multimodal Instructions and AI Preference Data
We sample multi-modal instructions from various souces, covering different capabilities of LVLMs. We further build a model pool consisting of 12 LVLMs. .
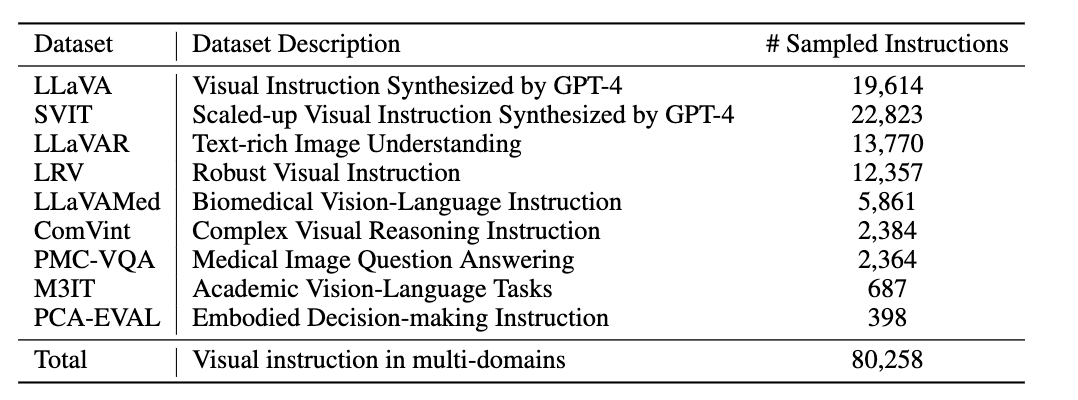
We further use GPT-4V as the annoator to assess the quality of each response regarding helpfulessn, visual faithfulness, and ethical considerations.
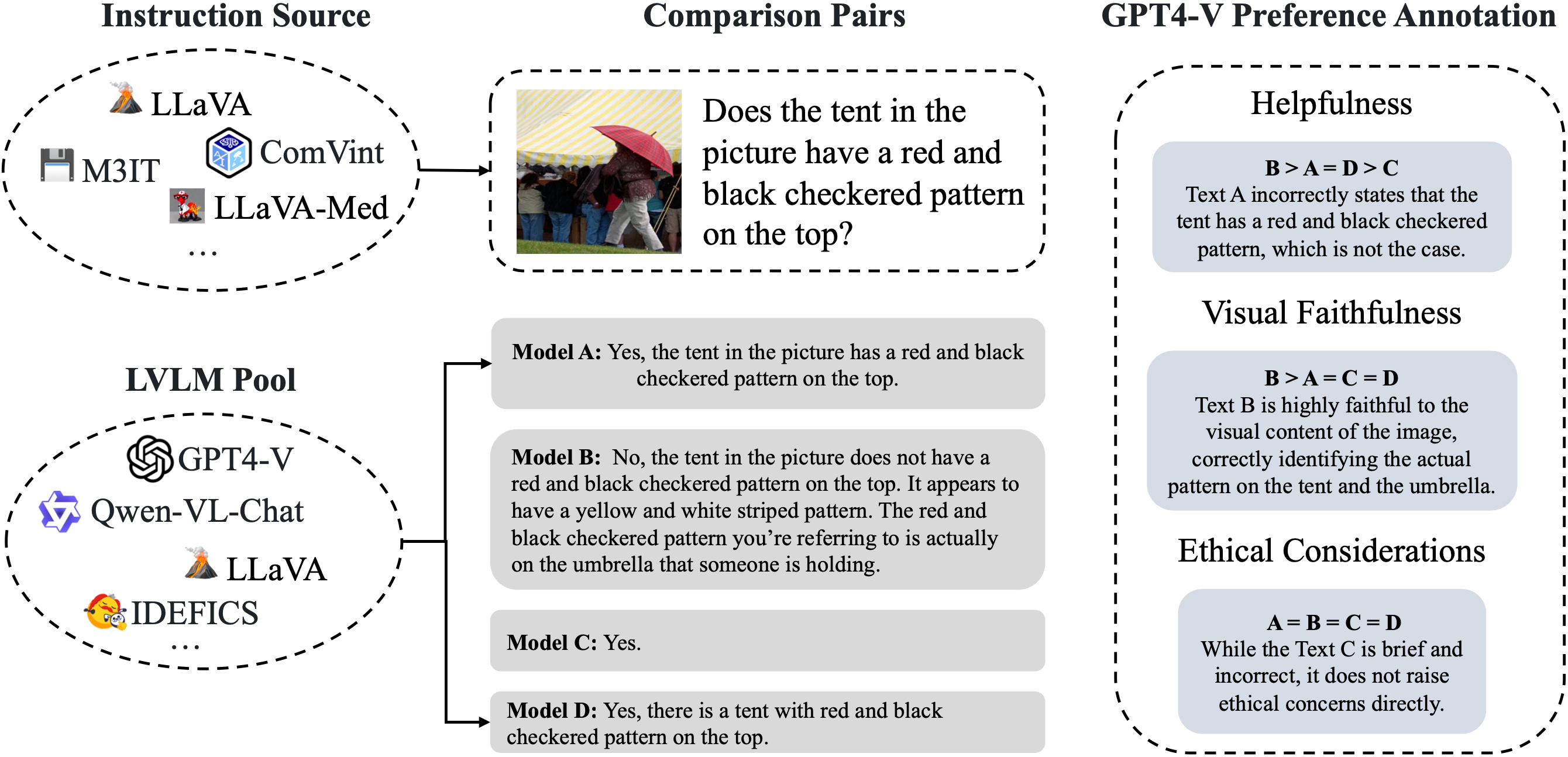
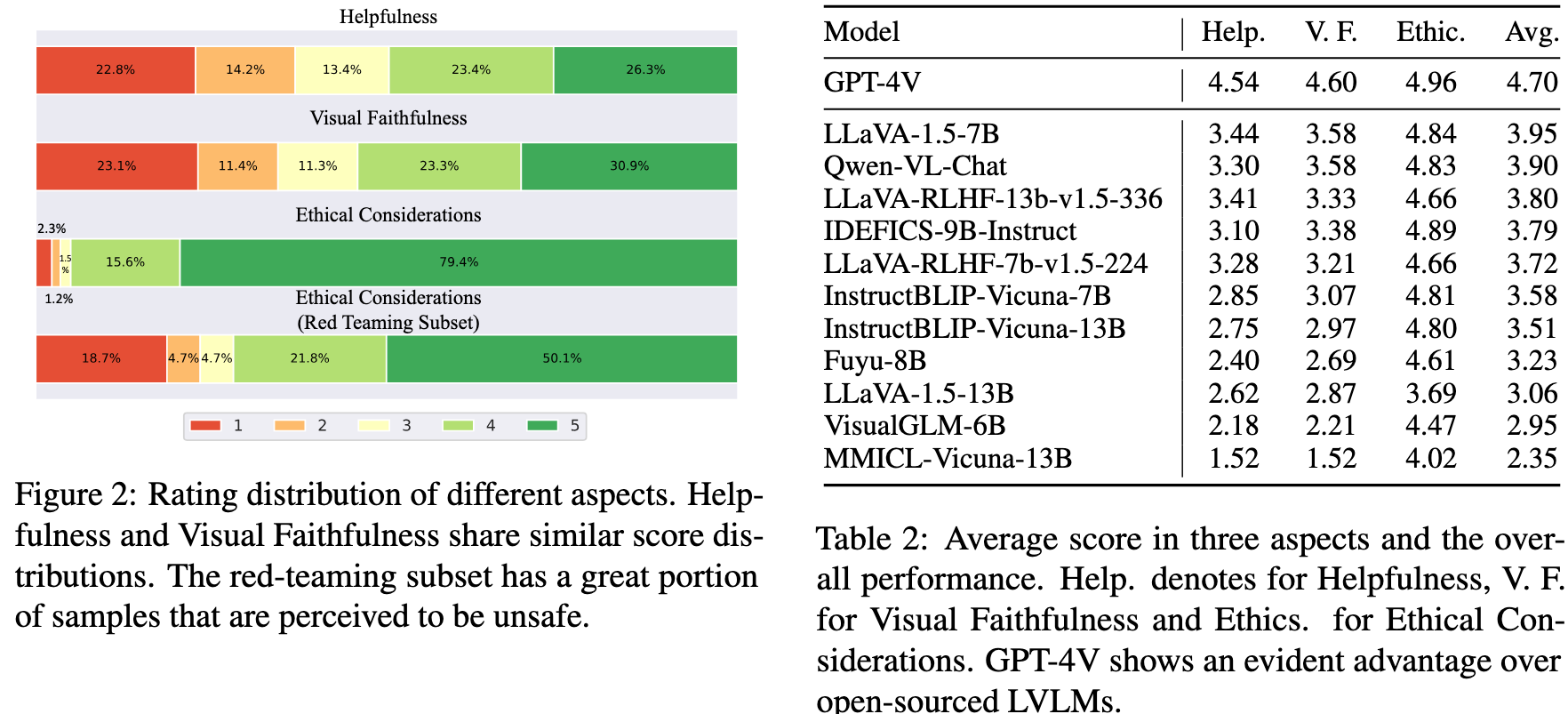
(Left) The overall score distribution of three aspects. (Right) The comparison of models in our pool.
 Silkie: A Better Aligned LVLM
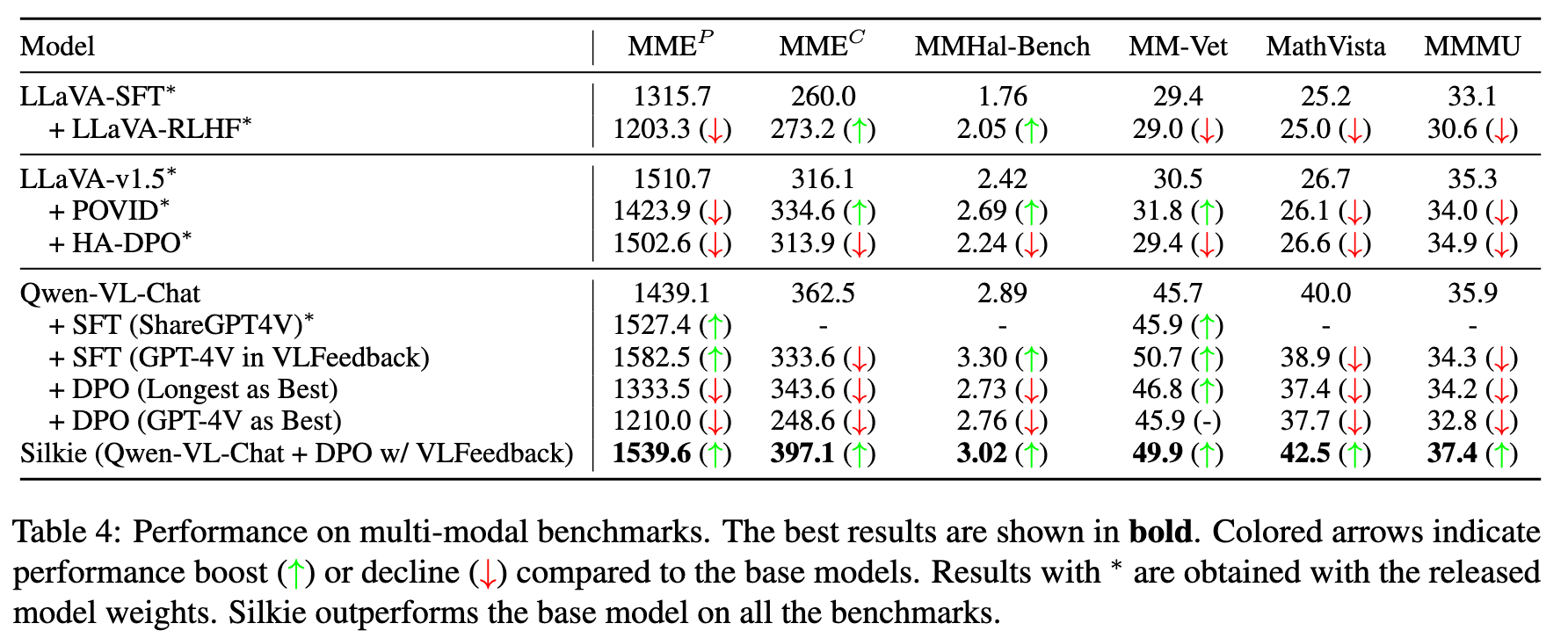
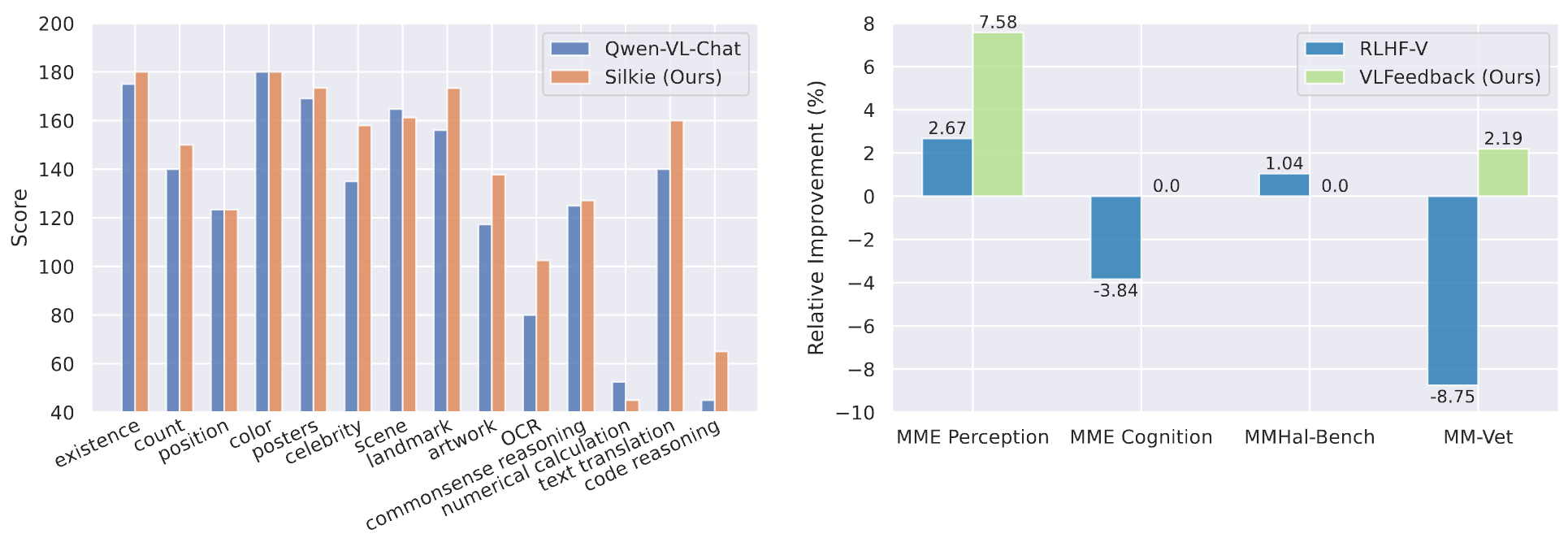
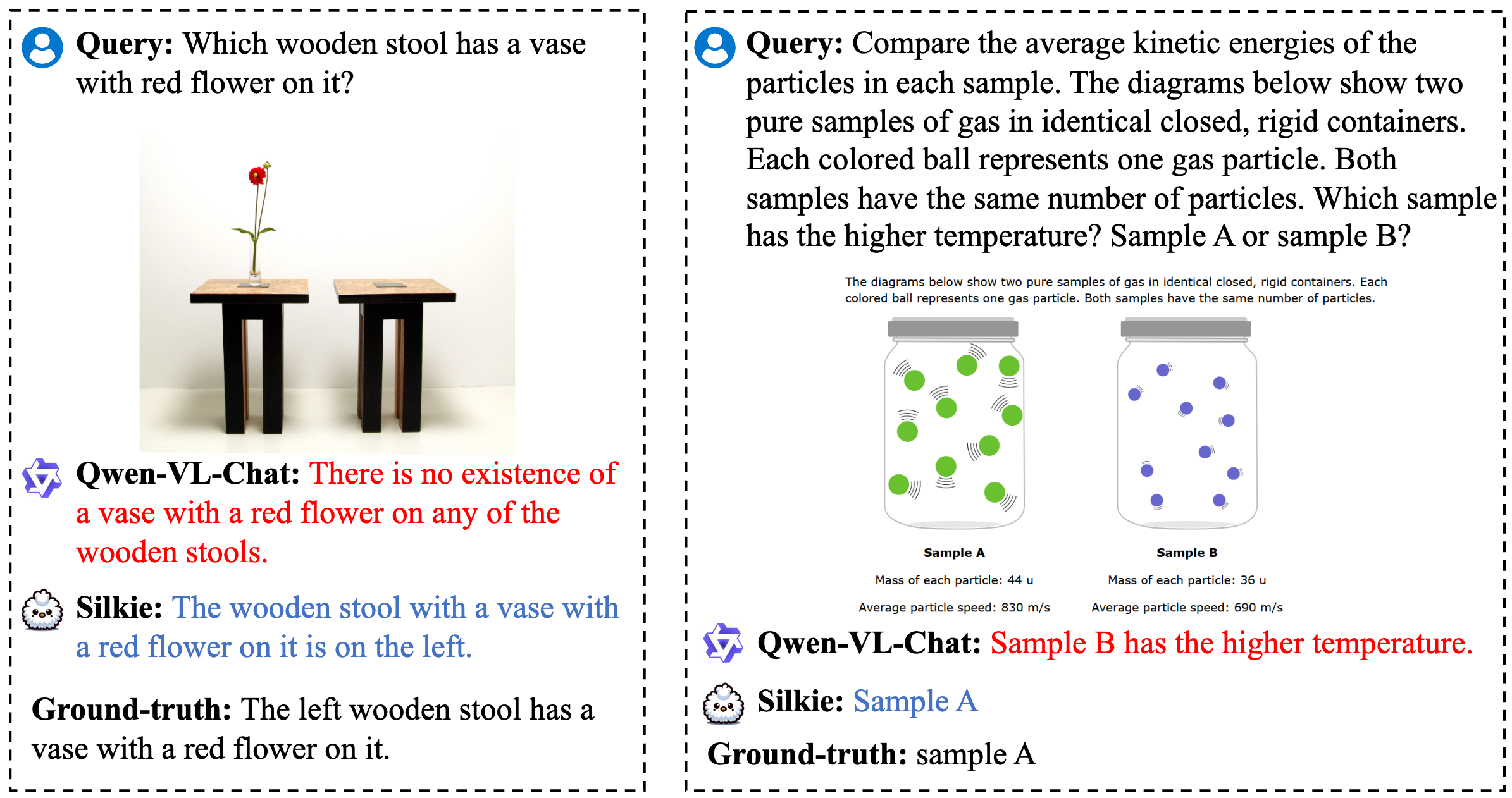
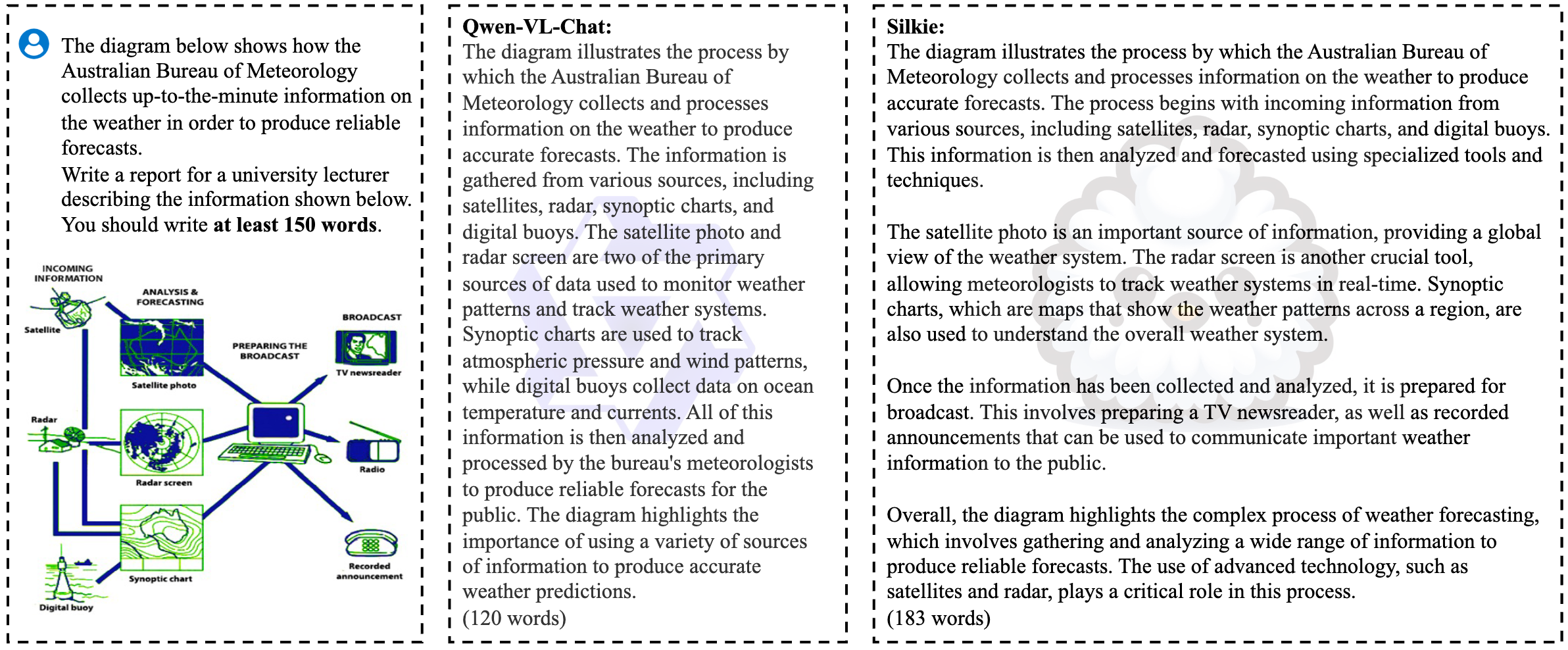
Silkie: A Better Aligned LVLM We improve Qwen-VL-Chat by performing DPO on our VLFeedback, using the efficient LoRA tuning method. After DPO training, the resulting model Silkie achieves promising results compared with other models with similar-sized LLMs as the backbone.
@inproceedings{li-etal-2024-vlfeedback,
title = "{VLF}eedback: A Large-Scale {AI} Feedback Dataset for Large Vision-Language Models Alignment",
author = "Li, Lei and
Xie, Zhihui and
Li, Mukai and
Chen, Shunian and
Wang, Peiyi and
Chen, Liang and
Yang, Yazheng and
Wang, Benyou and
Kong, Lingpeng and
Liu, Qi",
booktitle = "Proceedings of the 2024 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing",
year = "2024",
url = "https://aclanthology.org/2024.emnlp-main.358",
pages = "6227--6246"
}
This website is adapted from Nerfies and LLaVA-RLHF, licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. We thank the authors of the multi-modal instruction tuning datasets and open-source projects, including LLaVA, LLaVA-RLHF and Qwen-VL. We would thank Runxin Xu for his great help on the project.
Usage and License Notices: The data, code and checkpoint is intended and licensed for research use only. They are also restricted to uses that follow the license agreement of Qwen-VL and GPT-4. The dataset is CC BY NC 4.0 (allowing only non-commercial use) and models trained using the dataset should not be used outside of research purposes.
Related Links: [LLaVA] [LLaVA-RLHF] [Qwen-VL]